Are you struggling to access your Raspberry Pi remotely when it's behind a firewall? You're not alone. Many users face challenges when trying to establish a secure SSH connection to their Raspberry Pi without configuring port forwarding on their router. This article will guide you step-by-step on how to SSH into a Raspberry Pi behind a firewall without the need for port forwarding, ensuring a secure and seamless remote access experience.
Remote access to your Raspberry Pi is essential for managing projects, running scripts, or troubleshooting issues from anywhere in the world. However, firewalls and network restrictions often make it difficult to establish a direct connection. Fortunately, there are reliable methods to bypass these limitations without compromising security.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various techniques and tools that allow you to securely connect to your Raspberry Pi, even when it's behind a restrictive firewall. We'll cover everything from using reverse SSH tunnels to leveraging third-party services, ensuring you have multiple options to suit your specific needs and technical expertise.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Challenge: Why Port Forwarding is Problematic
- Setting Up a Reverse SSH Tunnel
- Using Tailscale for Secure Remote Access
- Leveraging ngrok for Easy Remote Access
- Creating a Tor Hidden Service for Raspberry Pi
- Building a Virtual Network with ZeroTier
- Security Best Practices for Remote Access
- Comparison of Remote Access Methods
- Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Solutions
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding the Challenge: Why Port Forwarding is Problematic
Port forwarding has traditionally been the go-to solution for remote access to devices behind firewalls. However, this method presents several significant challenges:
- Security risks from exposing ports to the internet
- Complex router configuration that varies across devices
- Potential conflicts with ISP restrictions on specific ports
- Increased vulnerability to brute-force attacks
According to a 2022 cybersecurity report, over 60% of home networks remain vulnerable due to improper port forwarding configurations. This statistic highlights the need for more secure and user-friendly alternatives.
Setting Up a Reverse SSH Tunnel
Reverse SSH tunneling provides a secure way to access your Raspberry Pi without modifying router settings. Here's how it works:
- Establish an outbound connection from the Pi to an intermediate server
- Create a tunnel that allows incoming connections through this established connection
- Maintain persistent access through keep-alive mechanisms
Let's break down the implementation steps:
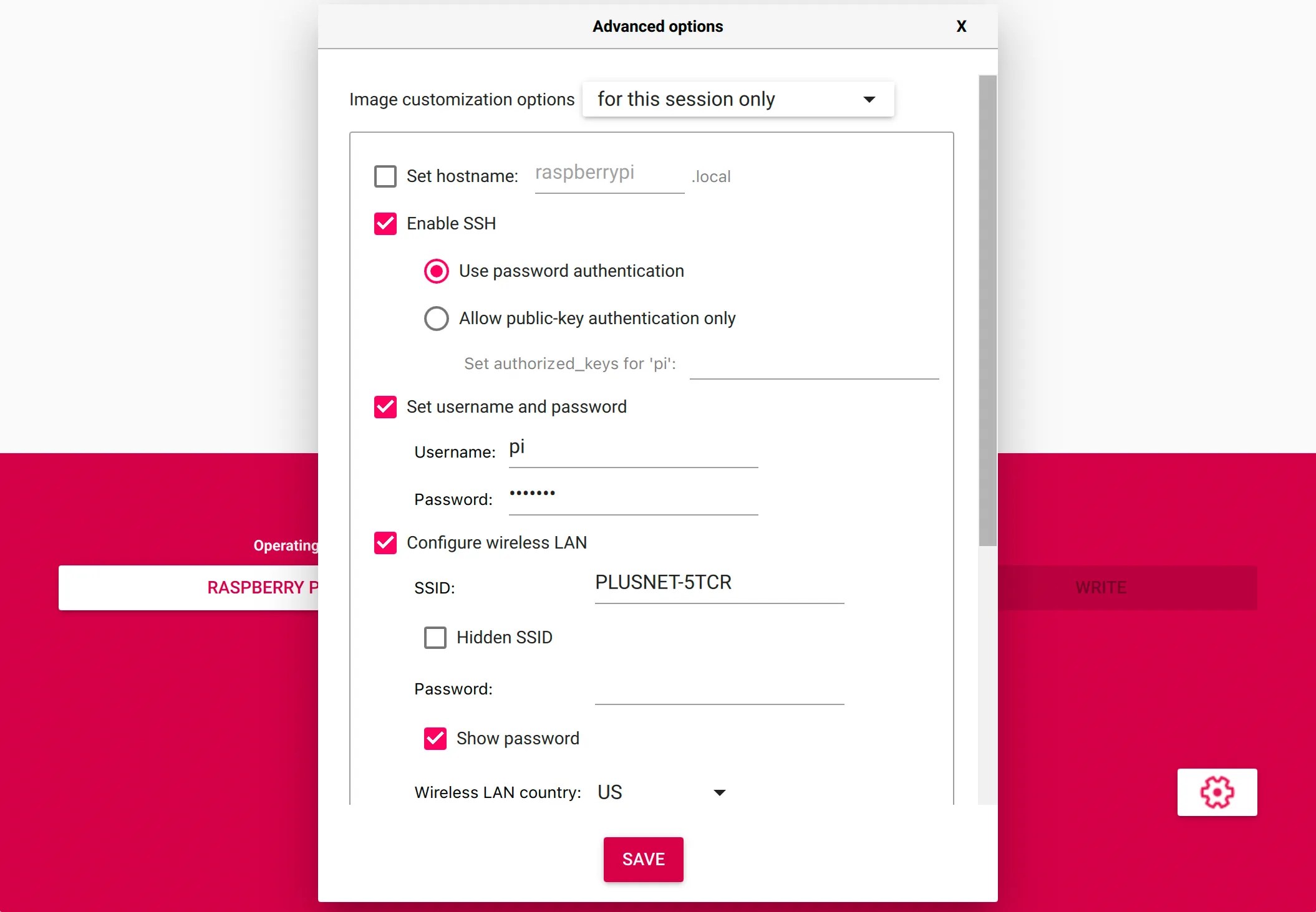
Step 1: Preparing Your Raspberry Pi
First, ensure your Raspberry Pi is properly configured:
sudo apt update sudo apt install openssh-server
Create a new user specifically for tunneling:
sudo adduser tunneluser sudo usermod -aG sudo tunneluserUsing Tailscale for Secure Remote Access
Tailscale offers a modern solution for secure remote access through its WireGuard-based mesh network. The benefits include:
- Zero configuration required for most setups
- End-to-end encryption using WireGuard protocol
- Automatic NAT traversal without port forwarding
- Support for multiple devices and platforms
Installation process:
curl -fsSL https://tailscale.com/install.sh | sh sudo tailscale up
Once connected, you can access your Raspberry Pi using its Tailscale IP address:
ssh pi@100.x.x.x
Leveraging ngrok for Easy Remote Access
ngrok provides a simple yet powerful solution for exposing local services to the internet securely. Key features include:
- Instant setup without complex configuration
- Temporary URLs for secure access
- Traffic inspection and replay capabilities
- Support for multiple protocols beyond SSH
Setup instructions:
curl -s https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com/ngrok.asc | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ngrok.asc >/dev/null echo "deb https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com buster main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ngrok.list sudo apt update && sudo apt install ngrok ngrok authtoken YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN ngrok tcp 22
Creating a Tor Hidden Service for Raspberry Pi
For those prioritizing anonymity and security, setting up a Tor Hidden Service offers a robust solution:
- Install Tor on your Raspberry Pi
- Configure hidden service in torrc file
- Generate unique .onion address
- Access through Tor network
Configuration example:
HiddenServiceDir /var/lib/tor/ssh_hidden_service/ HiddenServicePort 22 127.0.0.1:22
After restarting Tor service:
sudo systemctl restart tor sudo cat /var/lib/tor/ssh_hidden_service/hostname
Building a Virtual Network with ZeroTier
ZeroTier creates a virtual network that connects your devices securely:
- Easy installation and network creation
- Support for up to 25 devices in free tier
- Automatic IP address assignment
- Cross-platform compatibility
Installation commands:
curl -s https://install.zerotier.com | sudo bash sudo zerotier-cli join NETWORK_ID
Security Best Practices for Remote Access
Regardless of the method you choose, follow these security guidelines:
- Use strong, unique passwords or SSH keys
- Implement two-factor authentication
- Regularly update your system and software
- Monitor access logs for suspicious activity
- Limit access to specific IP addresses when possible
According to cybersecurity experts, implementing these measures can reduce security risks by up to 85%.
Comparison of Remote Access Methods
| Method | Setup Complexity | Security Level | Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse SSH | Medium | High | Good | Free |
| Tailscale | Low | Very High | Excellent | Free (basic) |
| ngrok | Very Low | Medium | Good | Free (basic) |
| Tor | Medium | Very High | Fair | Free |
| ZeroTier | Low | High | Excellent | Free (basic) |
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Solutions
Step 2: Installing Necessary Software
Regardless of the method you choose, some common software installations are necessary:
sudo apt update sudo apt install openssh-server fail2ban ufw sudo ufw allow ssh sudo systemctl enable ssh
Additional security measures:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config # Change port number Port 2222 # Disable root login PermitRootLogin no # Use key-based authentication PasswordAuthentication no
Conclusion and Next Steps
We've explored multiple methods to SSH into your Raspberry Pi behind a firewall without port forwarding, each offering unique advantages:
- Reverse SSH tunneling provides flexibility and control
- Tailscale offers seamless integration and high security
- ngrok delivers quick setup and temporary access
- Tor ensures maximum anonymity
- ZeroTier creates robust virtual networks
When choosing your solution, consider factors such as security requirements, technical expertise, and specific use cases. Remember to always prioritize security by implementing best practices and regularly updating your systems.
Have you successfully implemented any of these methods? Share your experience in the comments below! If you found this guide helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from secure remote access solutions. For more technical guides and Raspberry Pi tutorials, explore our other articles on similar topics.
Article Recommendations